China's AI trinity: How Alibaba, ByteDance, and Tencent are taking radically different paths to AI dominance
In this piece, we step back from the semiconductor world to focus on artificial intelligence - another major research area for Global Semi Research. Specifically, we examine the differentiated AI development strategies of China's three internet giants: ByteDance, Alibaba, and Tencent.
Our analysis centers on two key dimensions: model capabilities and practical application deployment. This piece serves as a foundational analysis and sets the stage for our ongoing coverage of how these major Chinese internet companies are positioning themselves in the AI landscape.
Model capabilities and strategic approaches
In terms of technological capability, Alibaba clearly leads the pack, ByteDance ranks second, while Tencent appears to be playing catch-up. However, Tencent's position doesn't necessarily indicate it's lagging in AI development overall, for reasons we'll explore.
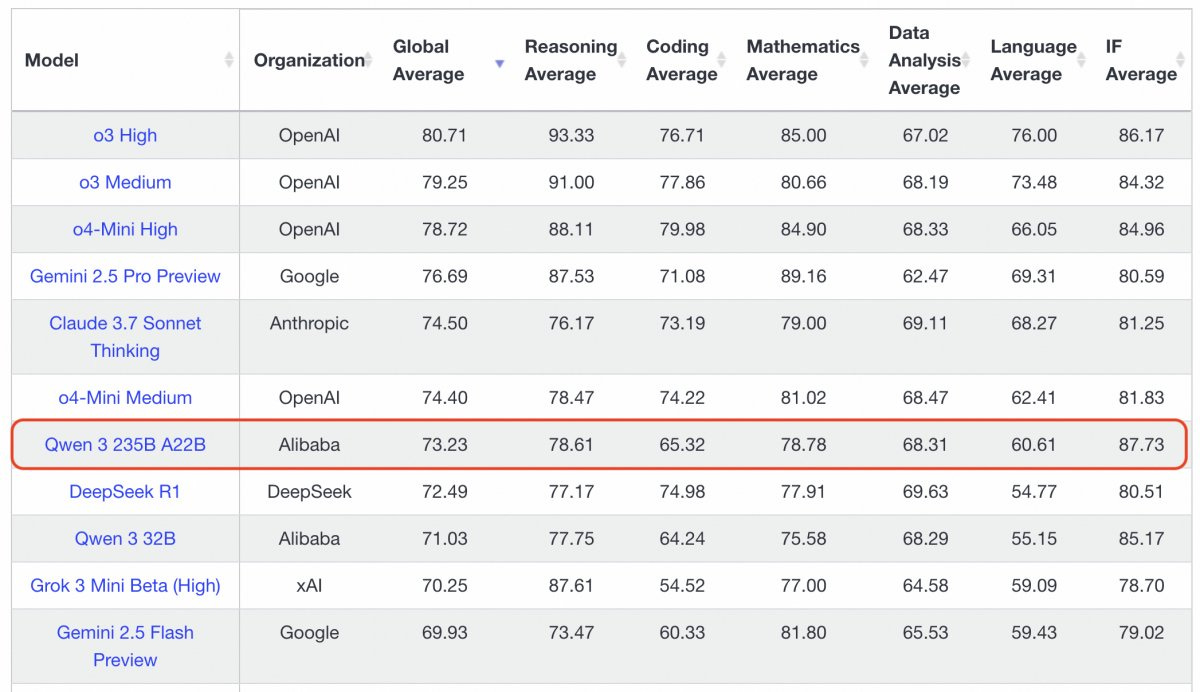
Building on its Qwen series, which released the latest Qwen 3 version in April, Alibaba has established itself as the global benchmark for open-source large language models. The high-performance, smaller-parameter models from the April release have particularly solidified Alibaba's position as the leader in open-source AI. Meanwhile, Alibaba demonstrates global ambitions with Qwen now supporting nearly 120 languages.
Through its open-source strategy, Alibaba aims to build an ecosystem around its platform by integrating the Qwen series into developer platforms like Hugging Face and Ollama, attracting global developers to co-create the ecosystem. This strategy has already yielded benefits in both business and enterprise markets, as well as in academic communities.
ByteDance focuses on developing its proprietary large language models. While the company has used other companies' foundational models to power products like its Cici chatbot (currently available primarily in Southeast Asia), it now concentrates on using proprietary models for application development. Its flagship model, Doubao, encompasses nine different model types covering text, voice, vision, and other capabilities.
Tencent's proprietary Hunyuan large language model has underperformed compared to peers, leading the company to focus on leveraging external models rather than heavily investing in Hunyuan's development. Tencent surprised many by becoming the first among Chinese tech giants to integrate DeepSeek into its product offerings, including WeChat—China's ubiquitous "super app" used daily by nearly every Chinese citizen for everything from messaging to payments.
This returns us to our earlier point: lacking a strong proprietary model isn't necessarily detrimental for Tencent, given its well-known product-first and user experience-first business approach. By integrating DeepSeek's R1 model, Tencent addressed Hunyuan's weaknesses in long-text reasoning and complex logical inference. The introduction of DeepSeek R1 into WeChat has significantly boosted usage of the app's search functionality.
Application deployment and market focus
For LLM implementation by major internet firms, we categorize their approaches into three areas: cloud services, applications, and agents. In terms of practical deployment, each company focuses on different aspects of these three categories.
Alibaba most closely resembles Amazon, both operating substantial cloud businesses. Alibaba's key commercialization strategy for LLMs centers on cloud services through model-as-a-service offerings. In terms of target customers, the company particularly focuses on smart hardware manufacturers, including smartphone and automobile companies, enabling these firms to integrate Alibaba's models into their products.
ByteDance focuses less on cloud services and more on applications and agents, aiming to integrate Doubao across its entire product portfolio. The company's apps—from Douyin (the mainland version of TikTok) to Toutiao—rank among China's most-used applications, with usage levels comparable to WeChat. Additionally, ByteDance has launched over 20 new standalone apps over the past two years, according to some estimates. These include the Doubao chatbot (named after its proprietary model) and Coze, a platform enabling developers to build applications.
Tencent's unique advantage lies in its WeChat app and 1.3 billion active users. This massive user base gives the company confidence to use third-party models rather than relying solely on its own—prioritizing product quality and user experience over model ownership, as long as the integrated models deliver optimal performance. By integrating DeepSeek into WeChat's search functionality, Tencent is using AI-powered search as an entry point to gradually expand its agent services network.
Strategic implications and future outlook
The AI strategies chosen by these three companies reflect their distinct understanding of the AI ecosystem. Alibaba uses open-source technology to define industry standards, ByteDance emphasizes proprietary development, while Tencent takes a more open approach by integrating third-party models for optimal results.
Alibaba builds technical communities through open-source initiatives. Its Qwen series not only supports local deployment but also offers multiple parameter versions to lower hardware barriers, attracting developers from vertical industries like legal and education. While this open ecosystem approach sacrifices short-term profits, it could establish standardized technological moats in the future.
ByteDance maintains a self-developed-first philosophy, controlling the entire process from model training to application deployment. The Doubao large language model doesn't use data generated by other models, and all business lines—including Douyin and Feishu, a Lark-like work collaboration app —prioritize integration with proprietary models, ensuring data sovereignty and consistent user experience.
Tencent's third-party empowerment strategy offers greater flexibility. This more open approach reflects the company's consistent product-first strategy. With WeChat as its foundation, Tencent may be positioned to develop AI agents fastest among the three firms. WeChat's optimal scenarios and AI search capabilities offer clear pathways toward agent-based product forms.